Imagine a trading scenario where decisions and outcomes unfold within hours, sometimes even minutes. In this article, we’ll provide an overview of what zero days to expiration options (0DTE) entail, discuss how they’re used, and examine strategies that traders may consider to navigate the complexities of this high-risk investment approach.
To get the most out of this guide, explore the following resources first:
What Are Zero Days To Expiration (0DTE) Options?
Days to expiration (DTE) represents the number of days left until an option contract expires. The expiration date plays a big role in determining the option's time value, which is a key part of the overall contract price. A 0DTE option can be defined as any contract that is being traded on the same day that the contract expires.
This option type may be appealing due to the inverse relationship between time to expiration (DTE) and an option's time value. This phenomenon, known as time decay or theta decay, accelerates as the expiration date nears. Theta is an option Greek which indicates the rate at which the option loses value as time passes.
Options with longer DTEs, such as 10DTE or 30DTE, exhibit greater time value due to the increased probability of the underlying asset's price fluctuating. Consequently, options with longer DTEs typically command higher premiums than 0DTE options.
How Do Zero Day To Expiration (0DTE) Options Work?
0DTE options offer traders the potential for efficient gains due to their reduced time value. This lower cost of entry, compared to options with longer DTEs, enhances potential leverage.
Consider an at-the-money (ATM) SPY call option with a $200 strike price. With 60 days to expiration, its premium might be $10 per share ($1,000 per contract). On the expiration day (0DTE), a similar ATM call's premium could be as low as $1.50 per share ($150 per contract).
While both options control 100 SPY shares (a notional value of $20,000), the 0DTE option's significantly lower premium offers greater leverage potential. This leverage stems from the reduced initial capital outlay relative to the underlying asset's exposure. There is also less time for the underlying security to potentially become in the money so there may be greater risk that you could lose the entire premium paid once the option expires.
How Market Conditions Can Affect 0DTE Strategies
Market conditions are crucial for 0DTE strategies, as these options are highly sensitive to rapid price changes. Intraday volatility, liquidity, and unforeseen market events can all exert substantial influence.
High-volatility environments typically inflate 0DTE premiums due to the increased potential for price swings. This attracts traders seeking to capitalize on intraday movements. However, higher volatility also brings greater risk, as sudden price reversals can lead to quick losses. In these conditions, 0DTE traders may sell options with high premiums to capitalize on time decay. The objective is to repurchase these options at a reduced price if volatility subsides, thereby profiting from the difference as accelerated theta decay erodes extrinsic value.
Conversely, during periods of low-volatility, price swings are typically smaller. This often results in reduced 0DTE premiums, which can limit profit potential from directional strategies. Low volatility environments may favor strategies that target smaller, more predictable price changes with a reduced risk of sudden market shifts. Additionally, the diminished rate of theta decay in such conditions may incentivize traders to adopt less aggressive or more defensively hedged positions.
The Role of Liquidity and Spreads for 0DTE vs. Longer DTE Options
High liquidity is essential for 0DTE options, as fast execution is critical for profitability. Tight bid-ask spreads (small difference between buying and selling prices) lower the additional implicit cost to the transaction, on top of the premium itself, allowing traders to enter or exit positions.
Unlike longer DTE options with steadier price moves and tighter spreads, 0DTE options experience rapid value changes. This heightened sensitivity to price changes and accelerated time decay often results in wider spreads. Navigating these liquidity conditions helps 0DTE traders avoid slippage and optimize their entries and exits.
What Are the Pros and Cons of Zero Day to Expiration (0DTE) Options?
While 0DTE options are a type of option trading strategy, it is not suitable for everyone. Below are both the benefits and risks of using 0DTE as a trading strategy.
Benefits of 0DTE Options
0DTE options present several potential advantages that have contributed to their increased adoption among traders:
- Greater Leverage: The reduced time value of 0DTE options translates to lower capital requirements for establishing positions with significant notional exposure. This leverage can magnify potential returns, albeit with commensurate risk.
- Fewer Transaction Costs: Due to accelerated time decay, 0DTE options often have lower premiums, reducing the upfront cost for traders because of the time decay.
- Agility in Response to Market Fluctuations: The short lifespan of 0DTE options enables traders to swiftly adjust their positions to intraday market dynamics, allowing for flexible management of sudden price movements.
- Increased Trading Opportunities: With new 0DTE options available daily and higher trading volumes, traders can enter and exit positions to potentially benefit from short-term market conditions.
A key advantage of 0DTE options for portfolio managers is the ability to implement precise and cost-effective hedging strategies. For active traders, 0DTE options offer a platform for frequent engagement with the market, allowing for the rapid iteration and refinement of trading strategies.
Risks of 0DTE Options
0DTE options carry the same risks as other options but add the challenge of a compressed trading timeframe. Option buyers must monitor price changes closely to react to sudden moves and likely make frequent transactions, while sellers face heightened risk of larger losses if prices shift sharply. Additionally, the short timeframe increases the chance that sellers may be assigned if buyers exercise before the market closes.
Risk Management Techniques:
- Position Sizing: Allocating only a small portion of capital to 0DTE trades can help limit potential losses. For example, limiting exposure to a small percentage of overall capital (e.g., 1%) per trade can mitigate potential losses.
- Stop-Loss Orders: Stop-loss orders limit losses by setting exit points. For instance, a trailing stop-loss adjusts to lock in gains as prices rise. However, while trailing stops can dynamically adjust to market movements, their sensitivity can lead to premature exits in volatile conditions. To reduce this risk, it's best to set stop-loss levels carefully, considering your profit-loss ratio and market volatility.
- Profit Targets: Establishing profit targets provides a disciplined approach to securing gains. This can involve utilizing limit orders or more complex strategies with predetermined exit criteria.
- Paper Trading: Simulated trading environments offer a risk-free platform for evaluating strategies and familiarizing oneself with the rapid dynamics of 0DTE options. For example, you can test your strategies using Alpaca’s paper trading environment.
Factors That Could Influence 0DTE Option Strategies
Traders using 0DTE options aim to capitalize on rapid time decay (theta decay) within a single trading day while managing significant risks. The effectiveness of these strategies depends on various factors and is typically favored by specific types of traders:
- Experienced Options Traders: These traders rely on a deep understanding of theta decay and price sensitivity, particularly for 0DTE setups where options lose value quickly.
- Risk-Conscious Traders: Seeking to balance income potential with defined risk, these traders avoid the high, unlimited risks of naked options by using structured spreads such as put verticals.
Several factors influence both the potential profitability and risk profile of 0DTE strategies:
- Delta Sensitivity (Price Sensitivity): Delta, a measure of an option's price sensitivity to changes in the underlying asset's price, serves as a critical indicator for 0DTE options. As expiration approaches and extrinsic value diminishes due to accelerated time decay, delta becomes a more accurate predictor of the probability of an option expiring in-the-money (ITM).
- Liquidity and Bid-Ask Spreads: Efficient execution is paramount in 0DTE trading due to the rapid pace of price movements. Liquid markets with tight bid-ask spreads minimize transaction costs and facilitate timely entry and exit.
- Volatility Levels: The level of implied volatility significantly impacts 0DTE option pricing and behavior. While moderate volatility can provide a favorable environment for capturing time decay, high volatility introduces greater risk due to potential price swings. Conversely, low volatility may limit profit potential.
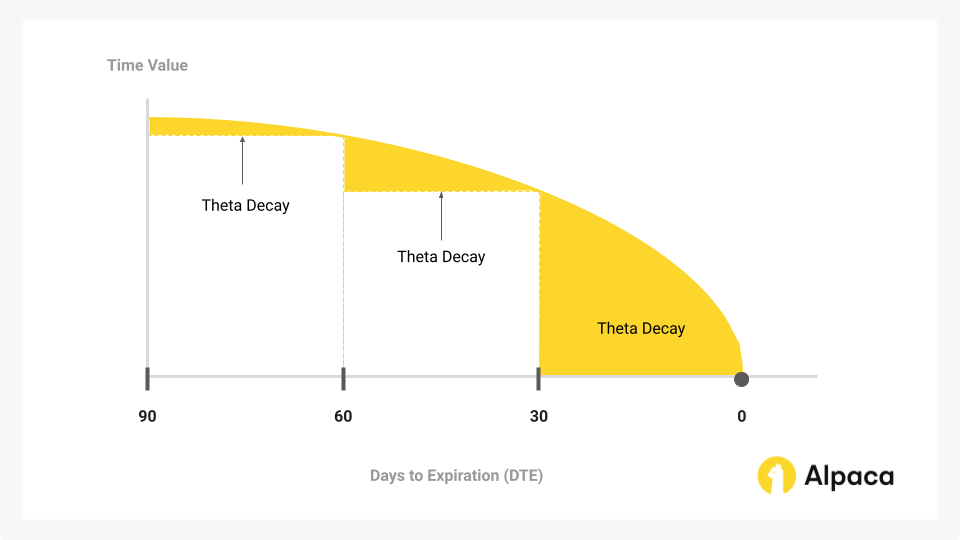
- Theta Decay (Time Decay): With little time left, 0DTE options undergo rapid theta decay, quickly reducing extrinsic value and the cost of the premium. Traders could potentially benefit by selling options early and buying them back at a lower price if the underlying price remains steady, though small price changes may still impact results and require close monitoring. Theta decay accelerates as expiration nears, shown in the diagram below, where the yellow area illustrates the shrinking time value with a sharp drop-off close to expiration.
What Are Some Examples of 0DTE Options Strategies?
0DTE options offer unique opportunities for traders who can capitalize on rapid intraday price movements and time decay. Here are some strategies commonly used.
Short Call Vertical Spreads
0DTE strategies frequently employ short positions to capitalize on premium capture and accelerated theta decay. Vertical spreads, which involve a combination of a short (sold) option and a long (bought) option at different strike prices, are commonly utilized. The short option's extrinsic value erodes more rapidly as expiration approaches, offering potential profit opportunities.
A short call vertical spread involves selling a call option that’s ATM or slightly out-of-the-money (OTM) while simultaneously buying a further OTM call option at a higher strike price. This bearish, directional strategy generates profit if the underlying asset's price stays below the short call strike price by expiration.
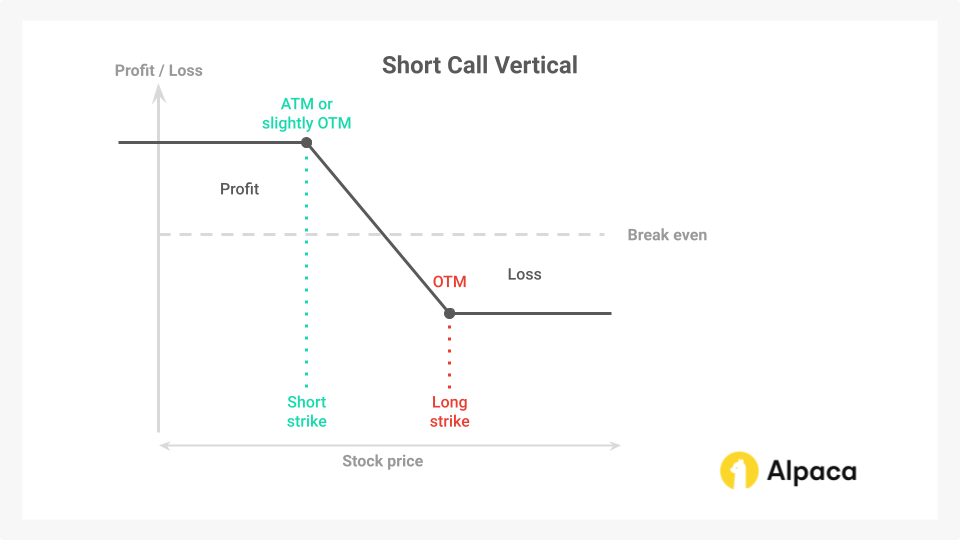
In this setup, both the sold and bought options lose value as expiration nears, with the sold option’s premium decaying more quickly, allowing the trader to potentially buy back the spread for less than the initial premium received.
Short Put Vertical Spreads
A short put vertical spread is established by selling a put option that is ATM or slightly OTM and simultaneously buying a put option with a lower strike price (further OTM). This bullish, directional strategy profits if the underlying asset's price remains above the short put strike price at expiration.
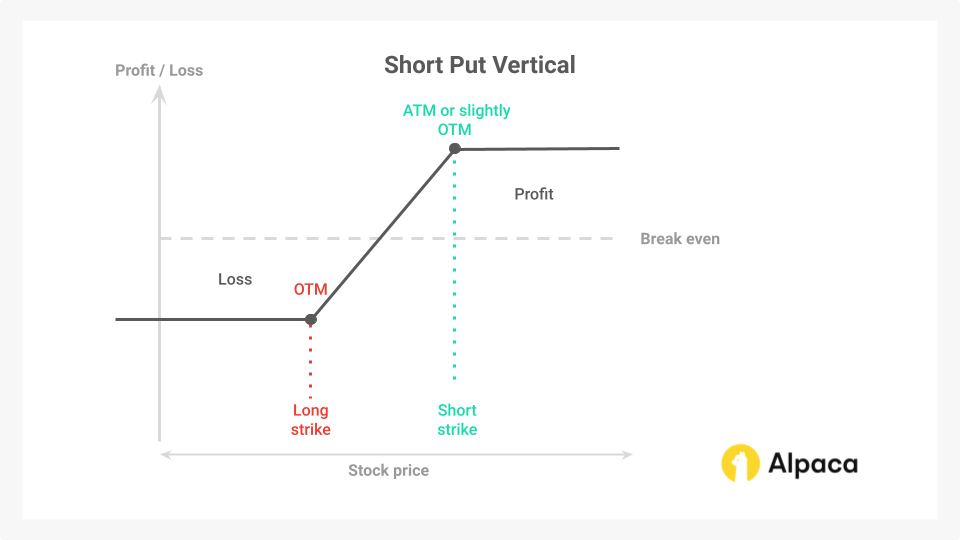
The profitability of this strategy stems from the accelerated time decay of the sold put option relative to the bought put option. If the underlying asset's price stays above the short put strike price, both options' extrinsic value erodes. However, the sold put option's value decays faster, potentially allowing the trader to close the spread at a net credit.
Iron Condor
The iron condor is an options strategy that involves the simultaneous purchase and sale of both call and put options (two puts and two calls, with one of each being bought and one of each being sold), each with distinct strike prices but identical expiration dates. This strategy is often employed in anticipation of low volatility.
Compared to a naked short strangle, the iron condor offers defined risk due to the inclusion of long options at the outer strike prices. These long options act as a hedge, capping potential losses while requiring a smaller capital outlay.
The construction of the iron condor strategy is as follows:
- Long Put: Purchase an OTM put option with a strike price below the current market price of the underlying asset. This put option acts as a hedge against significant downward price movement.
- Short Put: Sell an OTM or ATM put option with a strike price closer to the current market price.
- Short Call: Sell an OTM or ATM call option with a strike price above the current market price.
- Long Call: Purchase an OTM call option with a strike price further above the current market price. This call option acts as a hedge against significant upward price movement.
The iron condor's profit zone lies between the strike prices of the short put and short call options. The strategy's maximum profit potential is realized if the underlying asset's price remains within this range at expiration.
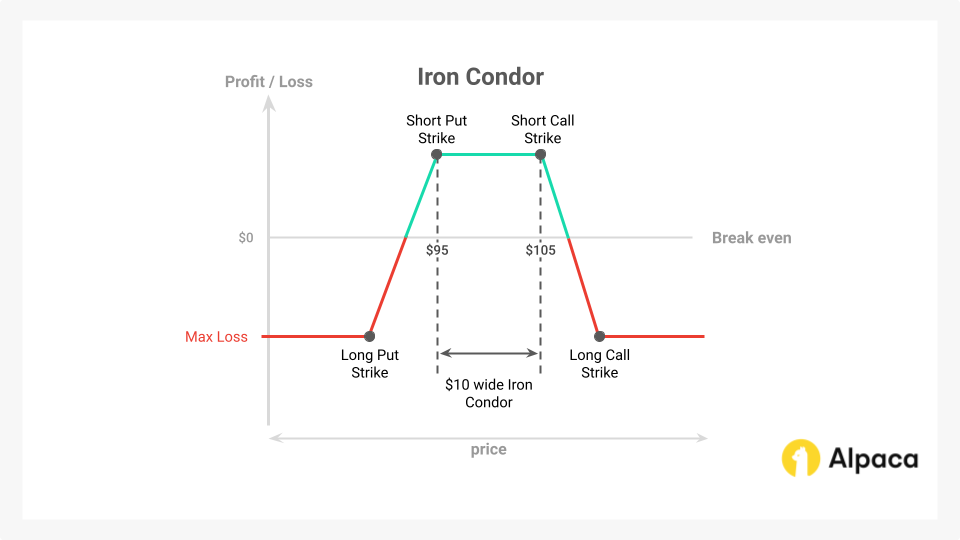
The iron condor can be visualized as a combination of a long strangle (long OTM put and long OTM call) positioned within a wider, short strangle (short OTM or ATM put and short OTM or ATM call).
Iron butterfly
The Iron Butterfly is a neutral options strategy that profits from decreased volatility and time decay. It employs four option contracts with different strike prices but the same expiration date. The strategy's effectiveness is amplified in a 0DTE context due to the accelerated theta decay and potential decline in implied volatility, which can optimize the position if the underlying asset's price remains stable.
Here’s how it’s structured:
- Sell an ATM Call: A short call option with a strike price near the current market price.
- Sell an ATM Put: A short put option with a strike price near the current market price.
- Buy an OTM Call: A long call option with a strike price higher than the ATM call.
- Buy an OTM Put: A long put option with a strike price lower than the ATM put.
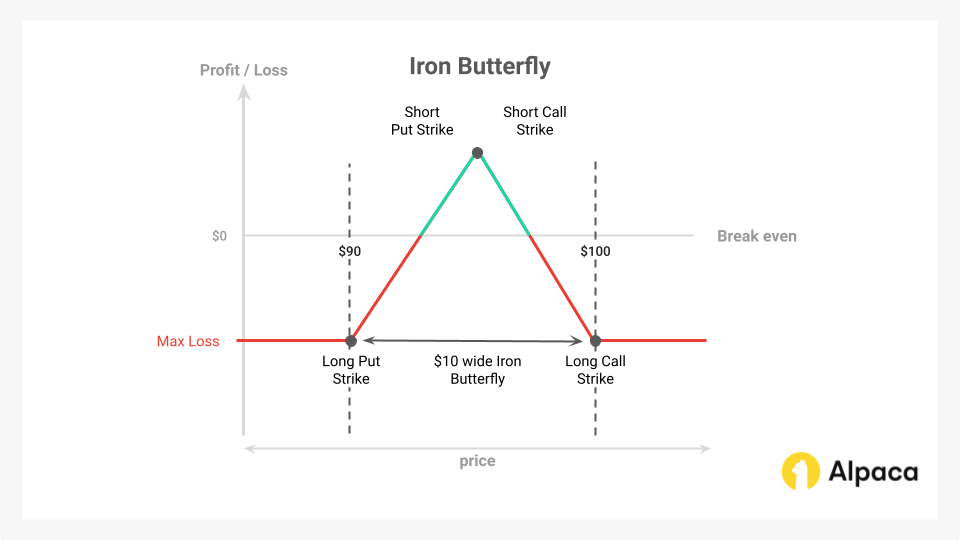
The maximum profit potential of the iron butterfly is realized if the underlying asset's price converges to the short strike prices at expiration. However, given the low probability of this precise outcome, traders often close the position early to secure profits or manage risk. A favorable outcome is achieved when the stock price remains stable or implied volatility decreases.
While 0DTE options offer enticing opportunities, it is important to recognize the inherent risks associated with these strategies. The compressed timeframe and heightened sensitivity to market fluctuations necessitate a comprehensive understanding of option mechanics, risk management principles, and diligent monitoring.
Traders are strongly encouraged to thoroughly evaluate their risk tolerance and employ prudent risk management techniques, including position sizing, stop-loss orders, and profit targets. Additionally, utilizing simulated trading environments (paper trading) can provide valuable experience and insights before deploying capital in live markets.
Is There a List of Securities That Offer 0DTE Options?
Popular underlying assets for 0DTE options include the SPX (S&P 500 Index), NDX (Nasdaq 100 Index), SPY (SPDR S&P 500 ETF Trust), and QQQ (Invesco QQQ ETF). While SPX, NDX, SPY, and QQQ are all popular underlying assets for 0DTE options, there are some key structural differences to be aware of:
- Underlying Asset & Settlement: Index options (SPX, NDX) are based on a basket of stocks and settle in cash at expiration. This means that profit or loss is simply a cash adjustment. On the other hand, ETF options (SPY, QQQ) are tied to funds that hold the actual underlying stocks. If exercised, these options result in the delivery of shares.
- Option Style: Index options are typically European-style, meaning they can only be exercised at expiration. ETF options are American-style, allowing for exercise at any point before expiration.
- Notional Value: SPX and NDX options carry high notional values, typically in the hundreds of thousands to over a million dollars per contract. In contrast, SPY and QQQ options have lower notional values (between $35,000 and $50,000), making them more accessible to retail traders.
Conclusion
In conclusion, 0DTE options offer traders a unique way to take advantage of the rapid decay of an option’s premium within a single trading day. These options provide lower upfront costs, increased leverage, and the flexibility to adjust positions quickly in response to intraday market shifts. Popular strategies for 0DTE options include theta decay techniques and structured spreads, where traders can use time decay while managing potential risks.
However, the short timeframe of 0DTE options increases both the potential for profit and the risk of loss, requiring close attention to price, liquidity, and volatility. Using techniques like conservative position sizing, trailing stop-loss orders, and clear profit targets can help manage these risks. Due to the fast-paced nature of 0DTE options, trading 0DTE options is best suited for experienced traders who understand options Greeks like theta and delta and can handle quick market changes.
For traders who can manage these factors, 0DTE options offer opportunities to refine strategies and utilize the market’s day-to-day fluctuations, making them an attractive but demanding tool in options trading.
Options trading is not suitable for all investors due to its inherent high risk, which can potentially result in significant losses. Please read Characteristics and Risks of Standardized Options before investing in options.
The Paper Trading API is offered by AlpacaDB, Inc. and does not require real money or permit a user to transact in real securities in the market. Providing use of the Paper Trading API is not an offer or solicitation to buy or sell securities, securities derivative or futures products of any kind, or any type of trading or investment advice, recommendation or strategy, given or in any manner endorsed by AlpacaDB, Inc. or any AlpacaDB, Inc. affiliate and the information made available through the Paper Trading API is not an offer or solicitation of any kind in any jurisdiction where AlpacaDB, Inc. or any AlpacaDB, Inc. affiliate (collectively, “Alpaca”) is not authorized to do business.
Please note that this article is for general informational purposes only and is believed to be accurate as of the posting date but may be subject to change. The examples above are for illustrative purposes only.
All investments involve risk, and the past performance of a security, or financial product does not guarantee future results or returns. There is no guarantee that any investment strategy will achieve its objectives. Please note that diversification does not ensure a profit, or protect against loss. There is always the potential of losing money when you invest in securities, or other financial products. Investors should consider their investment objectives and risks carefully before investing.
Securities brokerage services are provided by Alpaca Securities LLC ("Alpaca Securities"), member FINRA/SIPC, a wholly-owned subsidiary of AlpacaDB, Inc. Technology and services are offered by AlpacaDB, Inc.
This is not an offer, solicitation of an offer, or advice to buy or sell securities or open a brokerage account in any jurisdiction where Alpaca Securities are not registered or licensed, as applicable.